Asthma
Content:
- Definition
- Phenotypes
- Pathogenesis
- Sign / symptoms
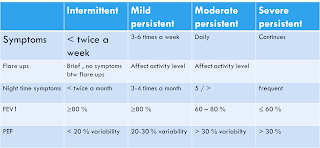
- Classification
- Diagnosis
- Medical Management
Definition:
Defined by the history of respiratory symptoms such as wheeze, shortness of breath, chest tightness & cough that vary over time & in intensity, together with variable expiratory flow limitation.
Variation is triggered by-exercise, allergen, irritant exposure, change in weather, viral respiratory infections.
Phenotypes:
- Recognizable clusters of demographic, clinical & / pathophysiological characteristics.
- Allergic asthma
- Non allergic asthma
- Late onset asthma
- Asthma with fixed airflow limitation
- Asthma with obesityobesity
Pathogenesis:
Symptoms:
- Wheeze , cough , shortness of breath , chest tightness.
- Symptoms occur variably over time ,vary in intensity.
- Worsen at night / on walking.
- Triggered by coldness, allergens , exercises.
- Appears /worsens with viral infections.
- Fever.
- Sputum production.
- H/o allergic rhinitis /atopic dermatitis.
- Family history
Sign:
- Tachypnoea , tachycardia.
- Use of accessory muscles.
- Wheeze – expiratory, audible.
- Silent chest.
- Percussion : hyper resonance.
- Altered mentation.
- Pulsus paradoxus
Life threatening:
Diagnosis:
- History and examination
- PEER
- Pulmonary function test: FEV1/FVC ratio
Normal >0.75 – 0.80 in healthy adults, >0.90 in children.
Excessive bronchodilator reversibility : FEV1 >12% .
- ABG- CO2 retention.
- Chest xray.
- CBC.
- Sputum examination.
- FENO – fraction of exhaled nitric oxide.
- predictor for exacerbation in allergic patients.
- Allergen testing.
Treatment:
- Oxygen – Sao2>90%
- SABA – inhaled/systemic.
- Costicosteroids - inhaled/systemic.
- Anticholinergics – ipratropium bromide.
- STATUS ASTHMATICUS
- Magnesium sulfate- 1-2 gm iv over 30 mins.
- Ketamine:0.2 mg/kg bolus.
- Methylxanthines.
- Ephinephrine
- LABA Leukotriene modifiers – montelukast , zaferlukast , zileuton.
- Mast cell modifiers – cromolyn , nedocromil.
- Immunomodulators : mepolizumab : IL5. omalizumab : block Ig E. Heliox







No comments:
Post a Comment