Foreign body obstruction
Epidemiology:
- Most airway foreign body obstruction occurs in Children younger than age of 15 yrs
- Children aged 1-3 yrs are the most susceptible
Etiology:
- They lack molars for proper grinding of food.
- They tend to running or playing at the time of aspiration.
- They tend to put objects on the mouth more frequently.
- They lack coordination of glottic and gastric closure.
Pathophysiology:
- Food items are aspirated most frequently
- Peanuts are most frequently aspirated items
- After foreign body aspiration occurs the foreign body can settle into 3 sites,
- That are larynx, trachea, bronchus.
Stages and phases for foreign body aspiration:
- Initial phase : chocking and gasping , coughing or airway obstruction or the time of aspiration.
- Asymptomatic phase: subsequent loading of the object with relaxation of reflexes that often result in a reduction or cessation of symptoms lasting hour to weeks.
- Complications phase : foreign body producing (erosion or obstruction) leading to pneumonia, atelectasis, or abscess.
Foreign body in the larynx:
- Laryngeal foreign body cause completely or partial airway obstruction.
Laryngeal foreign body symptoms:
Site:
- If the foreign body is retained for a longer period
- the following occur depending on the type of foreign body and duration:
- Accumulation of secretion
- Tracheitis or bronchitis with edema
- Swelling and granulation
- Bleeding and blood strained secretion
- Inspiratory and expiratory valvular stenosis
- Partial obstruction of the lower airway or emphysema
- Atelectasis or overinflation of the poststenotic part of the lung.
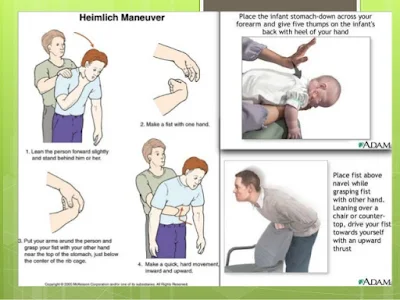
Treatment:
- Bronchoscopy (under general anaesthesia.


No comments:
Post a Comment